
Will the Universe expand forever?
The fate of the universe is determined by a struggle between the momentum of expansion and the pull of gravity. The rate of expansion is expressed by the Hubble Constant, Ho, while the strength of gravity depends on the density and pressure of the matter in the universe. If the pressure of the matter is low, as is the case with most forms of matter of which we know, then the fate of the universe is governed by the density. If the density of the universe is less than the "critical density", which is proportional to the square of the Hubble constant, then the universe will expand forever. If the density of the universe is greater than the "critical density", then gravity will eventually win and the universe will collapse back on itself, the so called "Big Crunch". However, the results of the WMAP mission and observations of distant supernova have suggested that the expansion of the universe is actually accelerating, which implies the existence of a form of matter with a strong negative pressure, such as the cosmological constant. This strange form of matter is also sometimes referred to as "dark energy". If dark energy in fact plays a significant role in the evolution of the universe, then in all likelihood the universe will continue to expand forever.
INFINITE UNIVERSE?
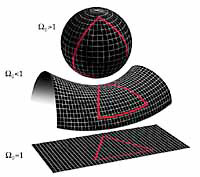 The density of the universe also determines its geometry. If the density of the
universe exceeds the critical density, then the geometry of space is closed and positively
curved like the surface of a sphere. This implies that initially parallel photon paths
converge slowly, eventually cross, and return back to their starting point (if the
universe lasts long enough). If the density of the universe is less than the critical
density, then the geometry of space is open (infinite), and negatively curved like the surface of a
saddle. If the density of the universe exactly equals the critical density, then the
geometry of the universe is flat like a sheet of paper, and infinite in extent.
The density of the universe also determines its geometry. If the density of the
universe exceeds the critical density, then the geometry of space is closed and positively
curved like the surface of a sphere. This implies that initially parallel photon paths
converge slowly, eventually cross, and return back to their starting point (if the
universe lasts long enough). If the density of the universe is less than the critical
density, then the geometry of space is open (infinite), and negatively curved like the surface of a
saddle. If the density of the universe exactly equals the critical density, then the
geometry of the universe is flat like a sheet of paper, and infinite in extent.
The simplest version of the inflationary theory, an extension of the Big Bang theory, predicts that the density of the universe is very close to the critical density, and that the geometry of the universe is flat, like a sheet of paper.
Measurements from WMAP
The WMAP spacecraft can measure the basic parameters of the Big Bang theory including the geometry of the universe. If the universe were flat, the brightest microwave background fluctuations (or "spots") would be about one degree across. If the universe were open, the spots would be less than one degree across. If the universe were closed, the brightest spots would be greater than one degree across.
Recent measurements (c. 2001) by a number of ground-based and balloon-based experiments, including MAT/TOCO, Boomerang, Maxima, and DASI, have shown that the brightest spots are about 1 degree across. Thus the universe was known to be flat to within about 15% accuracy prior to the WMAP results. WMAP has confirmed this result with very high accuracy and precision. We now know (as of 2013) that the universe is flat with only a 0.4% margin of error. This suggests that the Universe is infinite in extent; however, since the Universe has a finite age, we can only observe a finite volume of the Universe. All we can truly conclude is that the Universe is much larger than the volume we can directly observe.
